Acne Images
Click on images to enlarge.
Acne
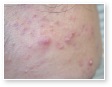
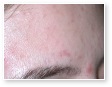
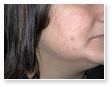
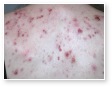
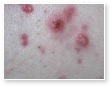
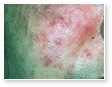
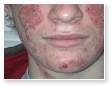
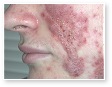
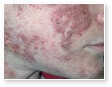
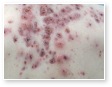
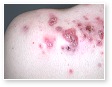
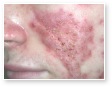
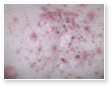
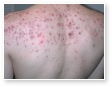
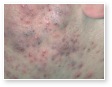
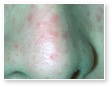
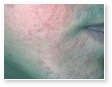
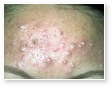
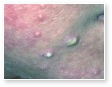
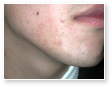
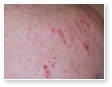
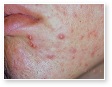
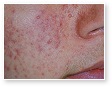
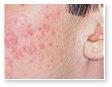
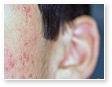
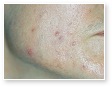
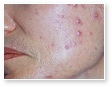
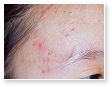
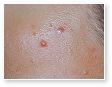
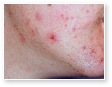
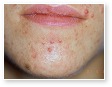
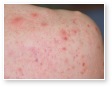
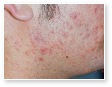
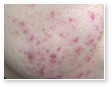
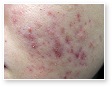
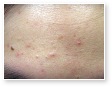
Acne Scars
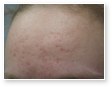
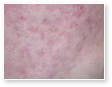
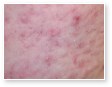
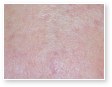
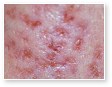

Different Types of Acne
Click on images to enlarge.
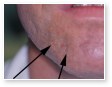
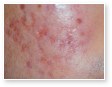
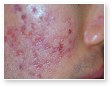
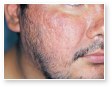
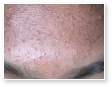
 Acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris is a disease of the sebaceous follicle. Increased production of oil in adolescence is associated with the development of comedones, erythematous papules, pustules, and, in some patients, cysts.
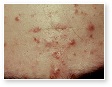
 Acne Agminata
Acne Agminata
Acne Agminata (Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei) is an eruption consisting of discrete yellow-brown to pink dome-shaped papules on the face and elsewhere that show a characteristic granulomatous histology.
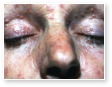
 Acne Conglobata
Acne Conglobata
This is a serious variant of acne with cyst and sinus formation associated with systemic signs, such as fever and malaise. Even with treatment, scarring can be quite severe.
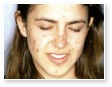 Acne Excoriee
Acne Excoriee
This is a severe exacerbation of acne conglobata to include much of the trunk and arms, which can be termed acne fulminans. These patients are quite ill, often with associated polyarthropathy.
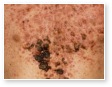 Acne Fulminans
Acne Fulminans
This is a severe exacerbation of acne conglobata to include much of the trunk and arms, which can be termed acne fulminans. These patients are quite ill, often with associated polyarthropathy.
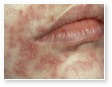 Drug Induced Acne
Drug Induced Acne
Glucocorticoids, androgens, anti-epileptic drugs, iodides, and isoniazids are relatively common causes of acne-like eruptions.
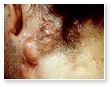
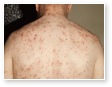 Endocrine Acne
Endocrine Acne
Excessive glucocorticoid or androgen production can be associated with severe acne.
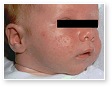 Neonatal Acne
Neonatal Acne
Neonatal acne is the development of typical acne lesions in neonates. At birth, the neonates' androgen levels are those of the mother. Typical lesions of acne can develop in a neonate in the two to three months postpartum.
 Chloracne
Chloracne
Chloracne follows exposure to chlorinated hydrocarbons. Most typically seen in an industrial setting, the eruption can be quite persistent.
Pustular Acne
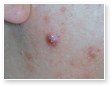
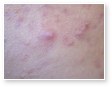
Acne Comedones
|